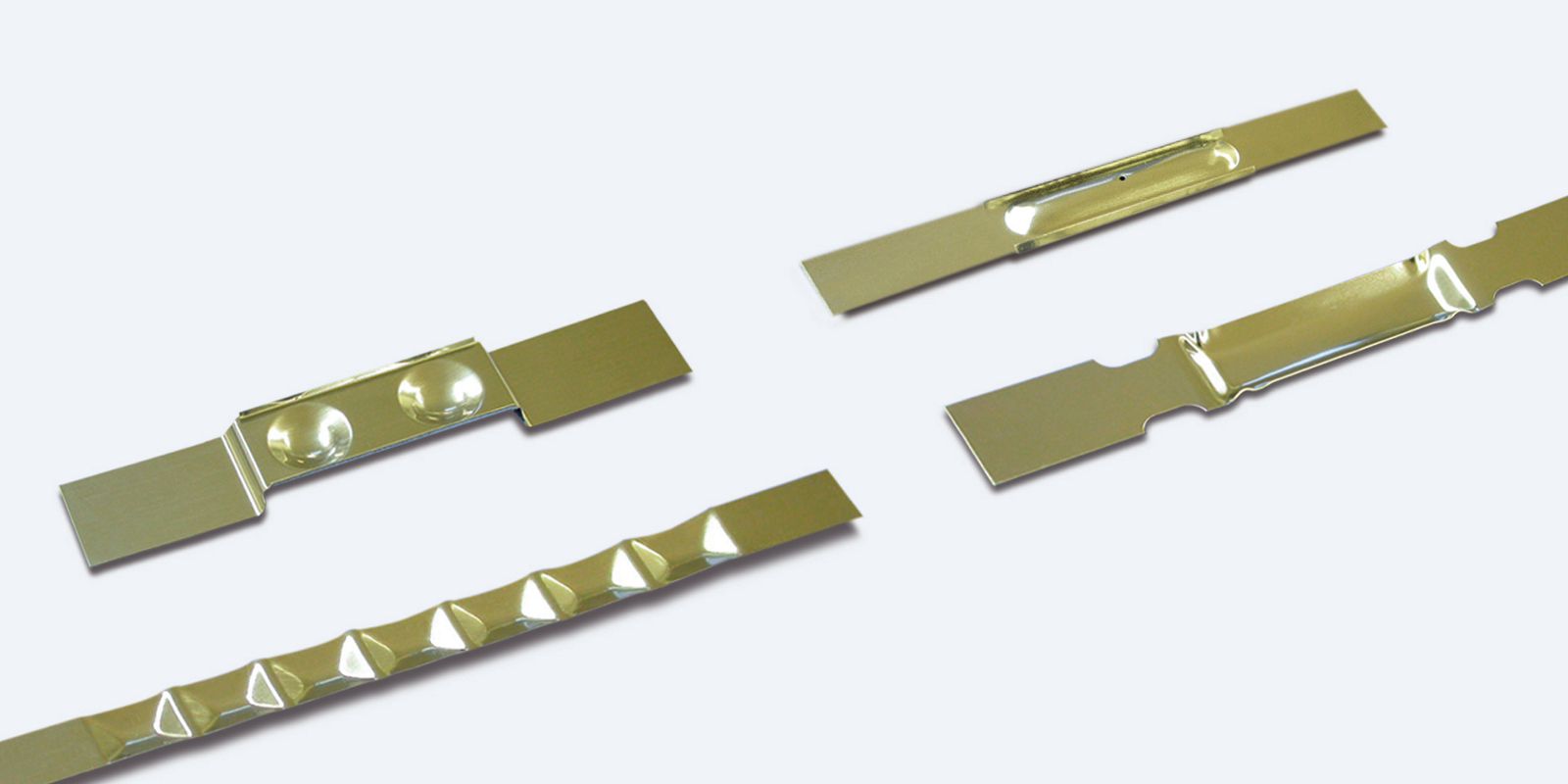
Evaporation boats
We manufacture evaporation boats made of tungsten, molybdenum, molybdenum-lanthanum (ML), molybdenum-yttrium oxide (MY), or tantalum for the resistance evaporation process. When current is applied, our boats heat the material to be evaporated. The low vapor pressures of our metals ensure that no tungsten, tantalum, or molybdenum particles enter the vapor and the final layer.
Your advantages at a glance:
Excellent
corrosion resistanceLow vapor pressures
Good electrical conductivity
Very high melting point
Dimensional stability

The thermal vacuum evaporation process (resistance evaporation) is a coating method and is one of the PVD (physical vapor deposition) processes. The material for the final layer is heated inside a vacuum chamber until it evaporates.
During the vacuum evaporation process, durable layers are produced from aluminum, silver, chromium, titanium nitride, or silica, for example. The result is sparkling watches, flawless mirrors, and high-quality electronic components. Also impressive are the long service life and high dimensional accuracy of our evaporation boats.
Our standard product range
We produce evaporation boats made of molybdenum, tungsten, and tantalum for your application:
Tungsten evaporation boats
Tungsten is highly corrosion-resistant compared with many molten metals and, with the highest melting point of all metals, is extremely heat-resistant. We make the material even more corrosion-resistant and dimensionally stable by means of special dopants such as potassium silicate.
Molybdenum evaporation boats
Molybdenum is a particularly stable metal and is also suitable for high temperatures. Doped with lanthanum oxide (ML), molybdenum is even more ductile and corrosion-resistant. We add yttrium oxide (MY) to improve the mechanical workability of molybdenum
Tantalum evaporation boats
Tantalum has a very low vapor pressure and a low evaporation speed. What is most impressive about this material, however, is its high corrosion resistance.

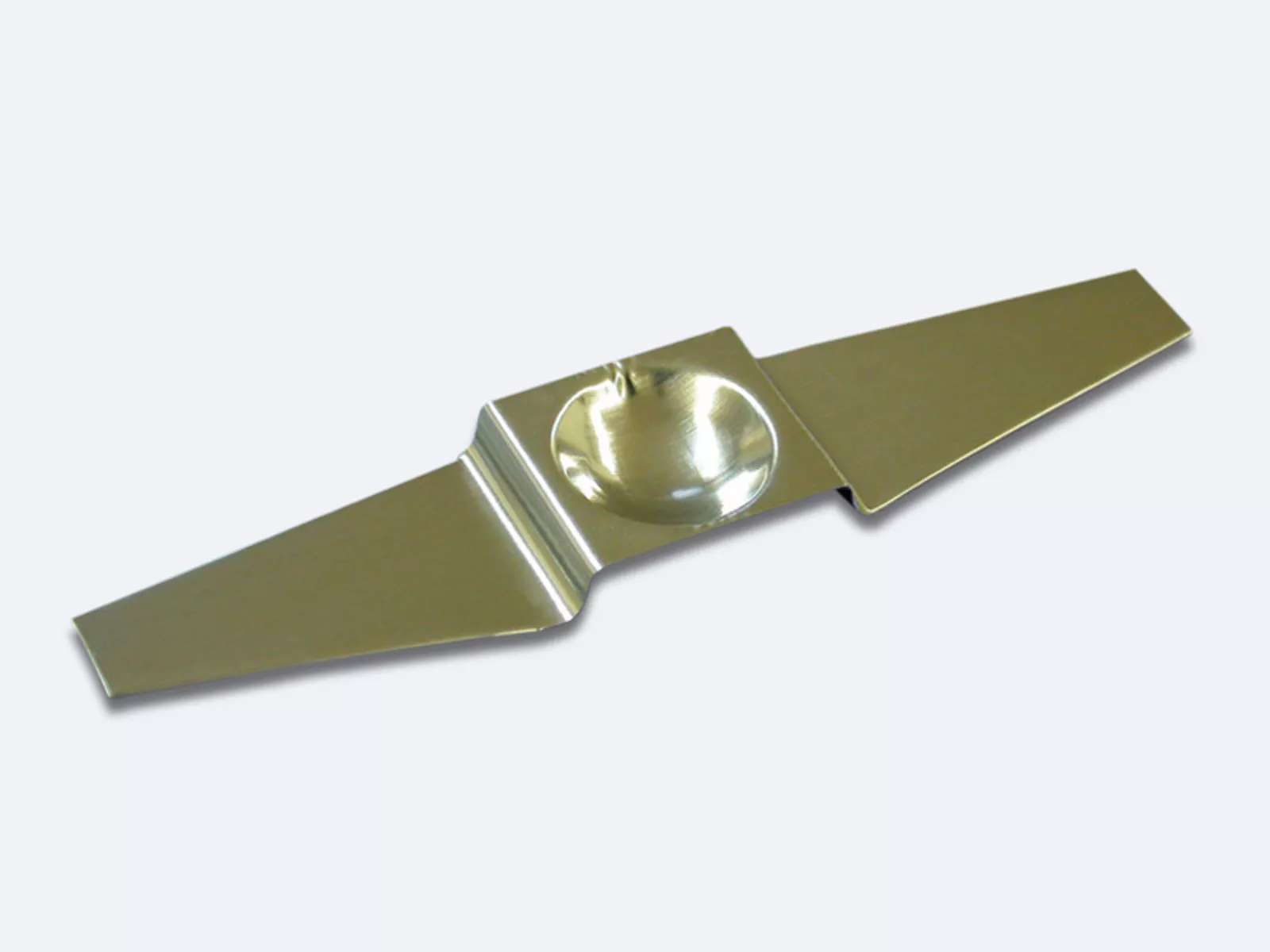
Straight type – straight boats

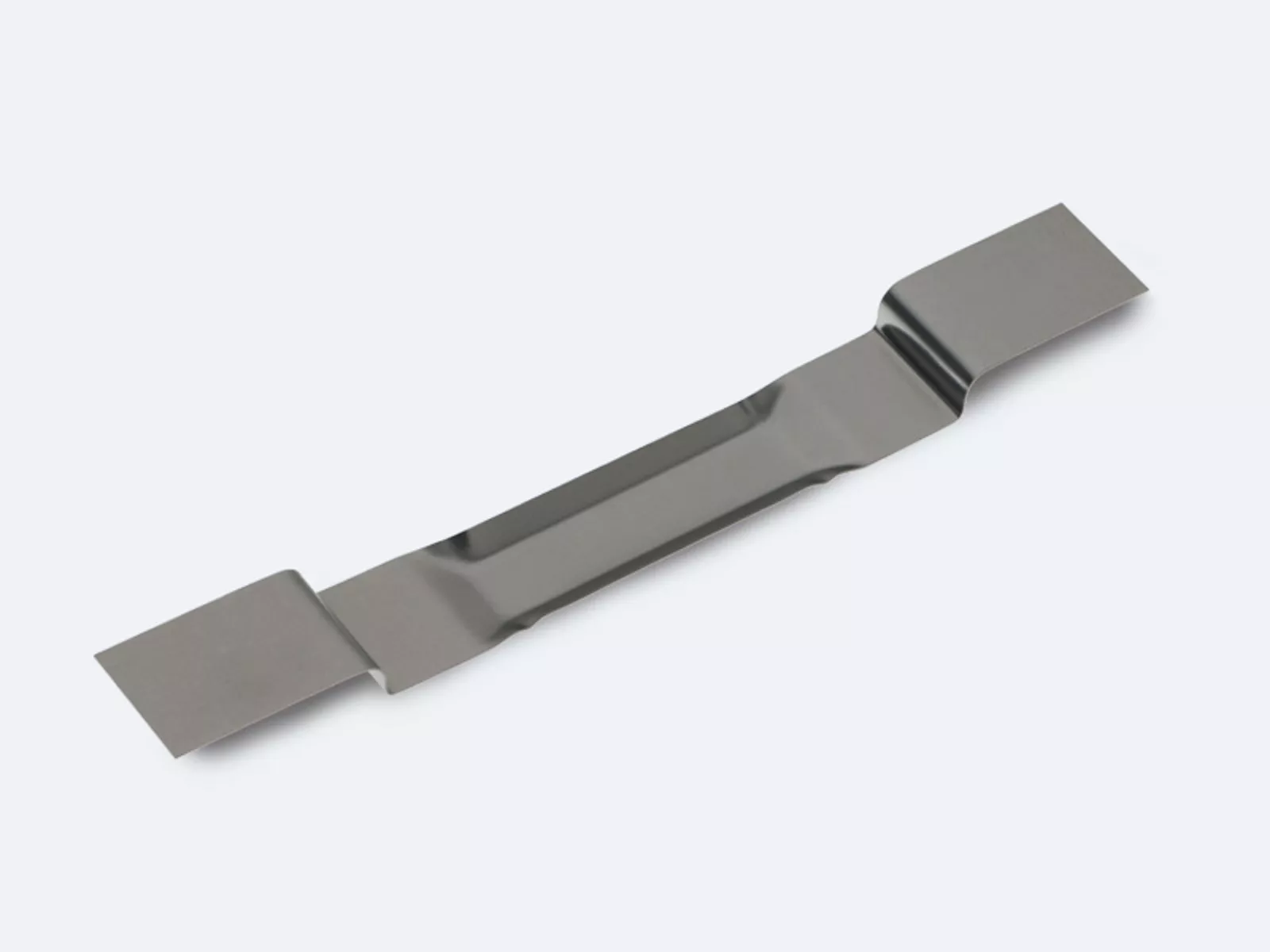
Step type – boats with a step between the clamping part and upper part
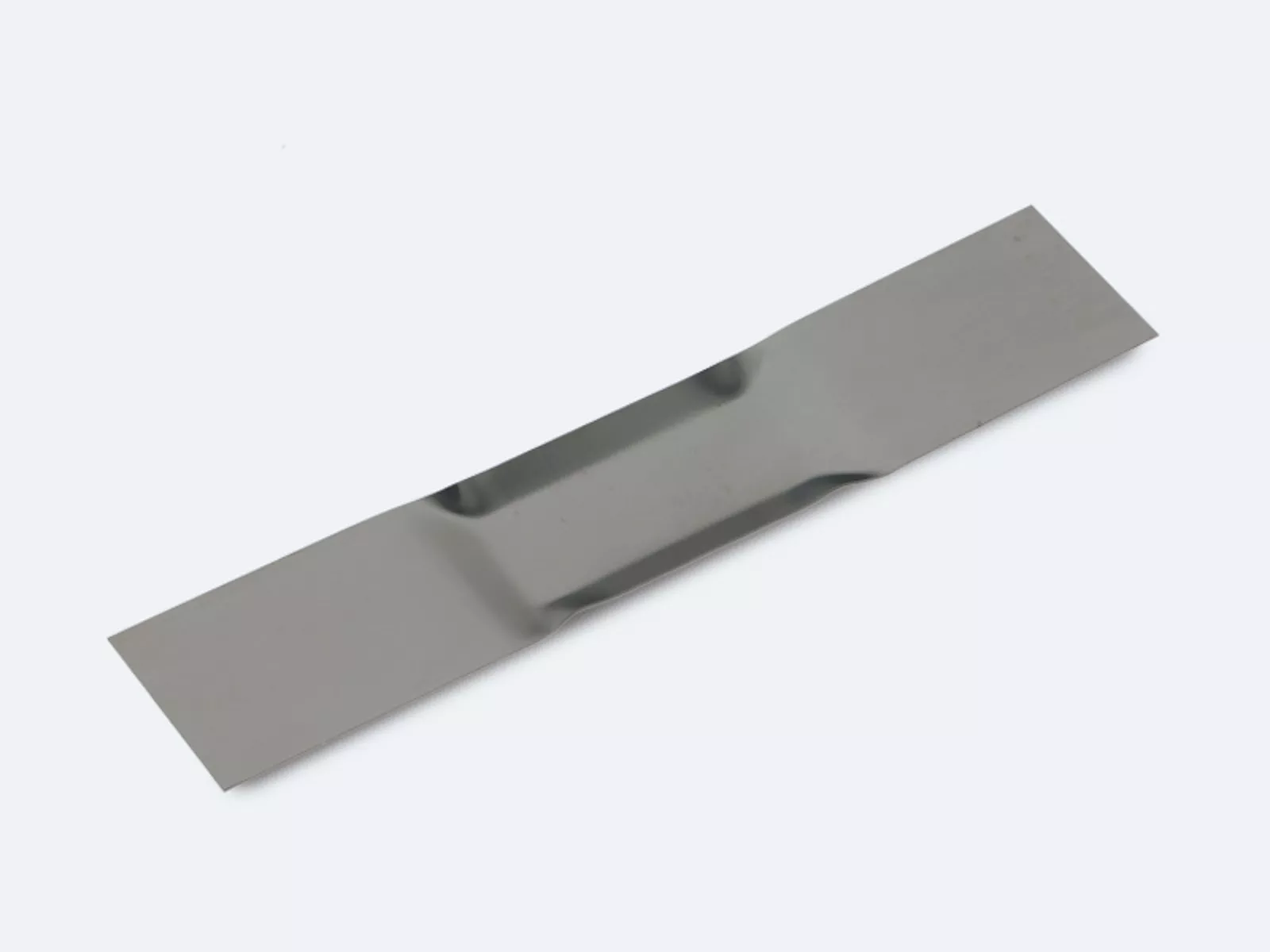

Non-splash type – boats with wings or a cover to minimize splashes
- Select the right boat for your coating material here
Das passende Schiffchen für Ihr Beschichtungsmaterial
Eine Übersicht der passenden Schiffchen für Ihr Material finden Sie hier. Schiffchen mit einem Plus eignen sich für das Material. Schiffchen mit zwei Plus empfehlen wir Ihnen ganz besonders. Gerne helfen wir Ihnen auch persönlich bei der Materialauswahl.
Beschichtungsmaterial Dichte
[g/cm³]Schmelzpunkt
[°C]Siedepunkt
[°C]Schiffchen W Mo Ta Al 2.7 660 2467 + AIF3 2.9 1291 N/A ++ ++ AI/1 – 4% Cu 2.7 650 N/A + AI/0.1 – 2% Si 2.7 640 N/A + AI/4% Cu/1% Si 2.7 640 N/A + Ag 10.5 961 2212 ++ ++ As2S3 3.4 300 707 ++ Au 19.3 1063 2966 ++ + B2O3 2.5 460 2247 ++ BaF2 4.9 1280 2260 ++ ++ ++ BaTiO3 6.0 1600 N/A + + BeO 3.0 2530 4120 + Bi 9.8 271 1560 ++ ++ ++ BiF3 5.3 727 900 ++ ++ Bi2O3 8.9 820 1890 + + CaF2 3.2 1360 2500 ++ ++ ++ CaO 3.3 2580 2850 + Cd 8.6 321 765 ++ ++ ++ CdSe 5.8 1350 N/A ++ ++ CdS 4.8 1750 1405 ++ ++ ++ CdTe 6.2 1042 N/A ++ ++ CeO2 7.1 2150 N/A ++ CeF3 6.2 1460 1987 ++ ++ Co 8.9 1495 2900 + ++ Cr 7.2 1875 2482 ++ Cr2C3 6.7 1850 3800 + Cr2C3 5.2 2345 4000 + Cu 8.9 1083 2595 ++ Cu2O 6.0 1235 1800 + DyF3 7.5 1155 1900 ++ ErF3 7.8 1144 1920 ++ Er2O3 8.6 2400 N/A + EuF3 6.7 1280 2270 + Eu2O3 7.4 2100 N/A + Fe 7.9 1536 3070 + Fe2O3 5.3 1594 N/A + Ga 5.9 30 2403 + GaAs 5.3 1238 N/A ++ GaP 4.1 1350 N/A ++ ++ ++ Ge 5.4 937 2830 + GeO2 4.2 1115 N/A ++ ++ ++ HfF2 7.1 1000 N/A ++ HoF3 7.6 1143 1895 ++ In 7.3 156 2000 ++ ++ In/10Sn 7.3 146 1000 + In2O3 7.2 2200 N/A + + LaF3 6.0 1495 2400 ++ ++ La2O3 6.5 2260 4200 + + LiF 2.6 842 1676 ++ ++ LuF3 8.3 1182 2200 ++ ++ Lu2O3 9.4 2400 N/A + ++ Mg 1.7 650 1107 ++ ++ ++ MgF2 3.1 1266 2239 ++ MgO 3.6 2640 3600 + Mn 7.4 1245 2097 + ++ ++ MnS 4.0 1615 N/A + + MoO3 4.7 795 1155 ++ MoS2 4.8 1185 N/A ++ Na3AIF6 2.9 1000 N/A ++ ++ Na5AI3F14 3.0 1027 N/A ++ ++ NaF 2.6 988 1695 ++ ++ ++ NdF3 6.5 1377 2400 ++ ++ Nd2O3 7.2 2240 N/A + Ni 8.9 1453 2732 + Ni/Cr 7.5-8.5 1500 N/A + Nb 8.6 2468 4927 + Nb2O5 4.5 1512 N/A + Pd 12.0 1552 2927 + Pt 21.5 1769 3827 + PrF3 6.3 1399 2255 ++ ++ Pr2O3 7.1 2270 N/A + Rb 1.5 39 688 + SmF2 6.6 1306 2323 ++ Sm2O3 7.1 2325 N/A + ScF3 2.6 1530 1800 ++ Sc2O3 3.9 2400 N/A + Se 4.8 217 685 + + + Si 2.3 1410 2355 + SiO 2.1 1705 1880 ++ ++ Sn 7.3 232 2260 ++ ++ SnO2 6.9 1127 1850 + + SrF2 4.2 1450 2489 ++ ++ Ta2O5 8.3 1880 N/A + Te 6.2 450 1390 ++ ++ ++ TbF3 7.2 1172 2280 + Tb2O3 7.9 2300 N/A + + ThF4 6.3 1100 1680 ++ ++ Ti 4.5 1668 3260 + TiO2 4.2 1775 2700 + TiO 4.9 1750 3000 ++ Ti2O3 4.6 1760 N/A ++ V 6.1 1900 3410 + + WO3 7.2 1473 N/A ++ Y 4.5 1509 2927 ++ YF3 5.1 1155 2210 ++ YbF3 8.2 1157 2136 ++ ++ Yb2O3 9.2 2346 N/A + Zn 7.1 420 907 ++ ++ ++ ZnSe 5.4 1526 N/A ++ ++ ++ ZnS 4.1 1850 1665 ++ ++ ZnTe 5.5 1238 N/A ++ ++ Zr 6.5 1852 3578 + ZrF4 4.4 600 908 ++ ZrO2 5.6 2700 4300 + ZrO 6.4 2200 N/A ++
The exact dimensions can be found in our shop:
Evaporation speed and vapor pressure
Our materials for evaporation boats have a very low evaporation speed at evaporation temperature and an extremely low vapor pressure compared with the coating materials. This means that no boat material enters the layer, even in the case of long evaporation cycles.
Specific electrical resistance
The specific electrical resistance is an important variable when it comes to the design of evaporation boats.
Order evaporation boats from stock in the Plansee online shop
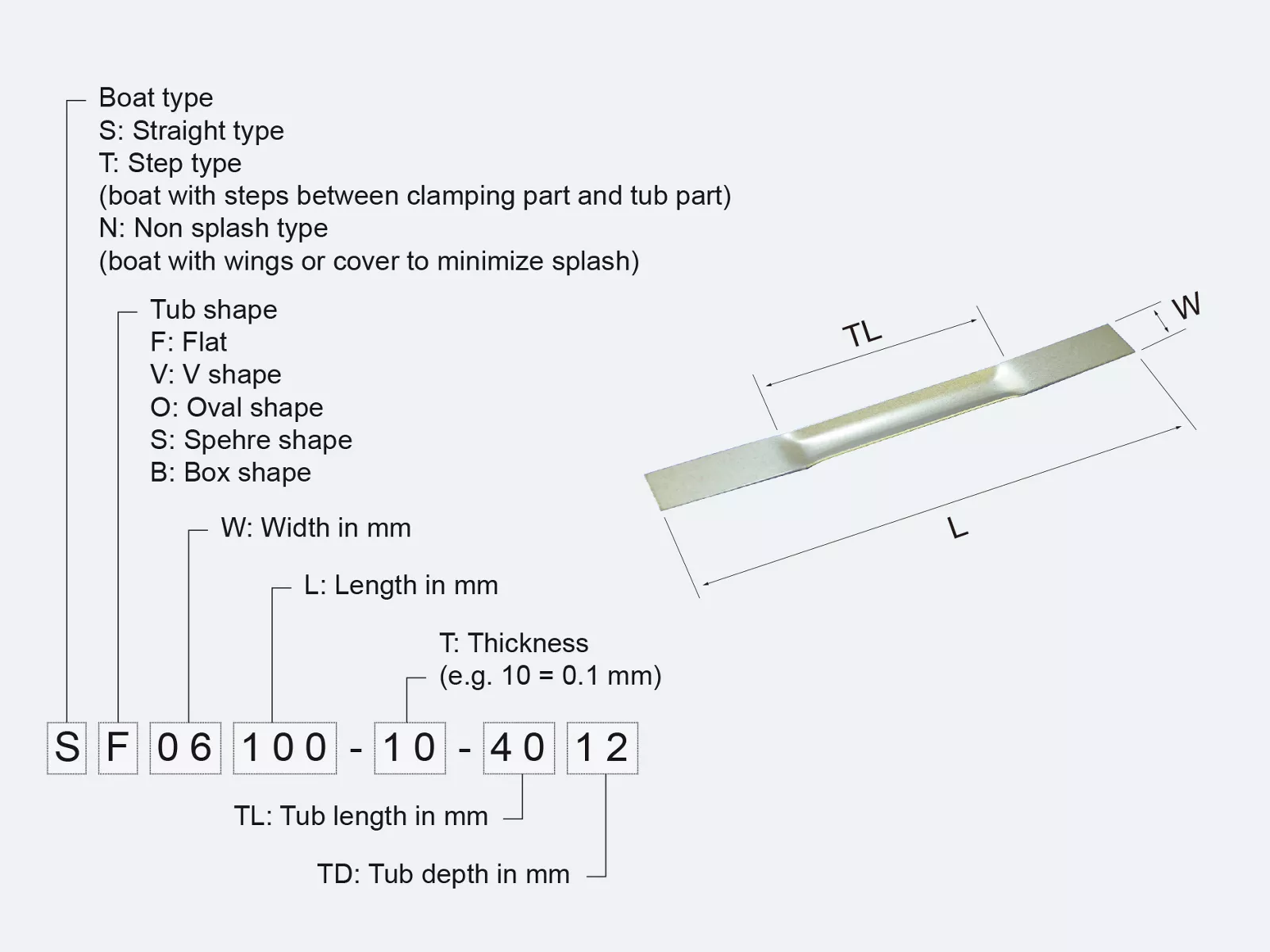
Item numbers for evaporation boats
More detailed information regarding our tungsten, molybdenum, and tantalum evaporation boats can be derived from the item number. This is formulated as follows:
Further components for your coating process
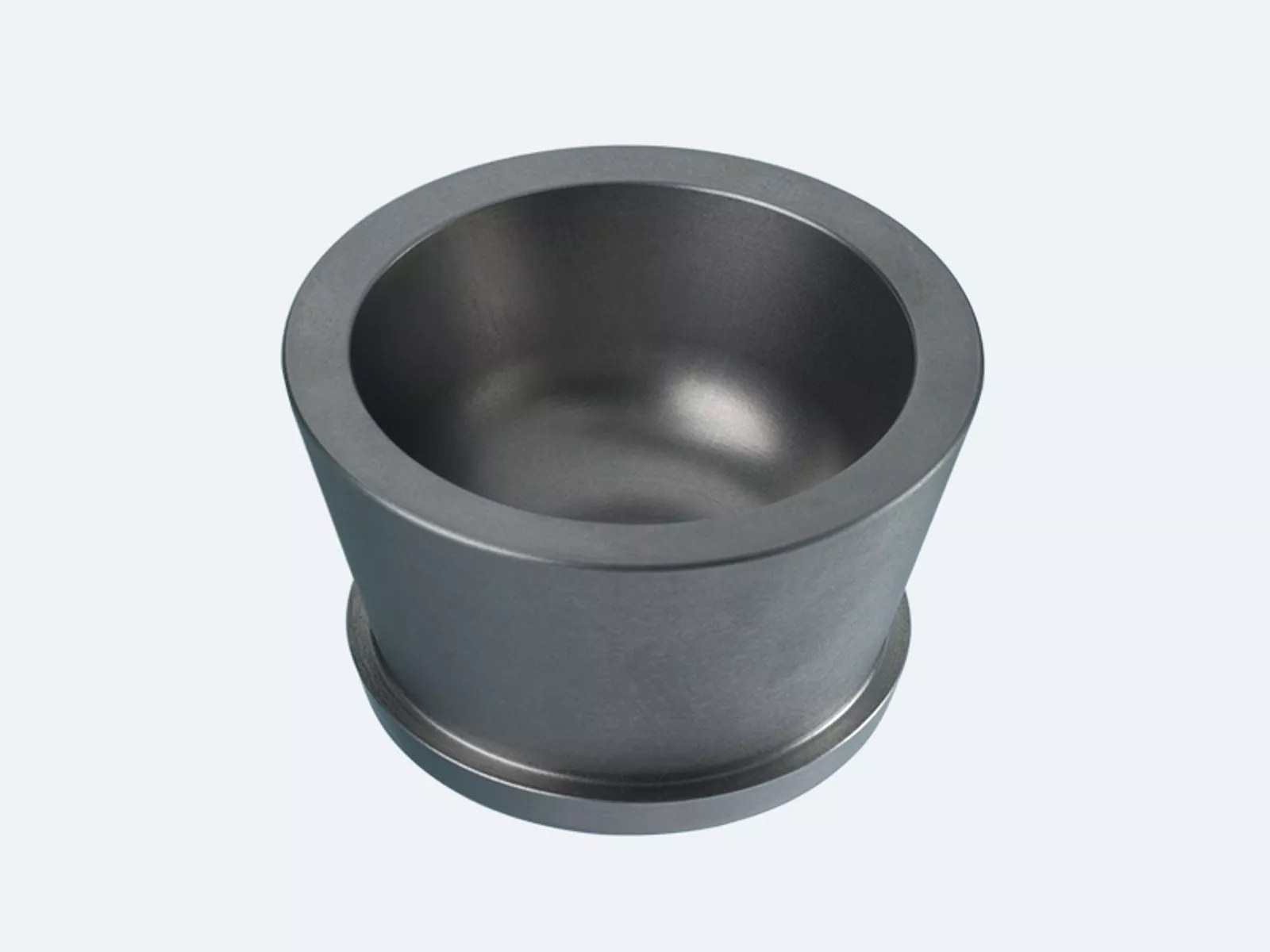

We provide crucible inserts made of molybdenum, tungsten, and tantalum for electron beam evaporation. Unlike copper and graphite crucibles, these do not contaminate your evaporation material. We'll be happy to optimize the geometry and material composition of our crucibles to suit your coating process.
Our tungsten and molybdenum filaments are used in electronic resistance evaporation.


