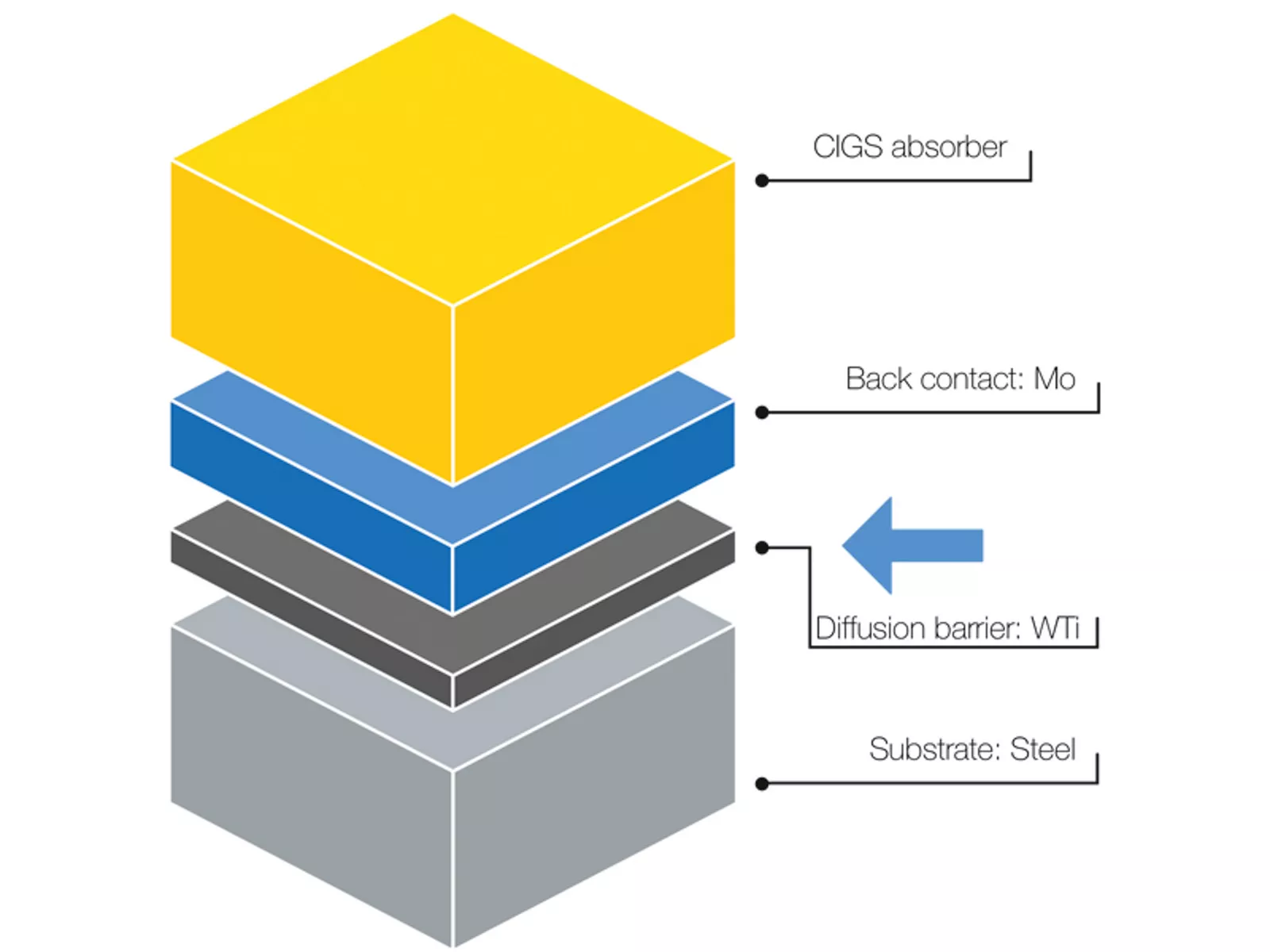
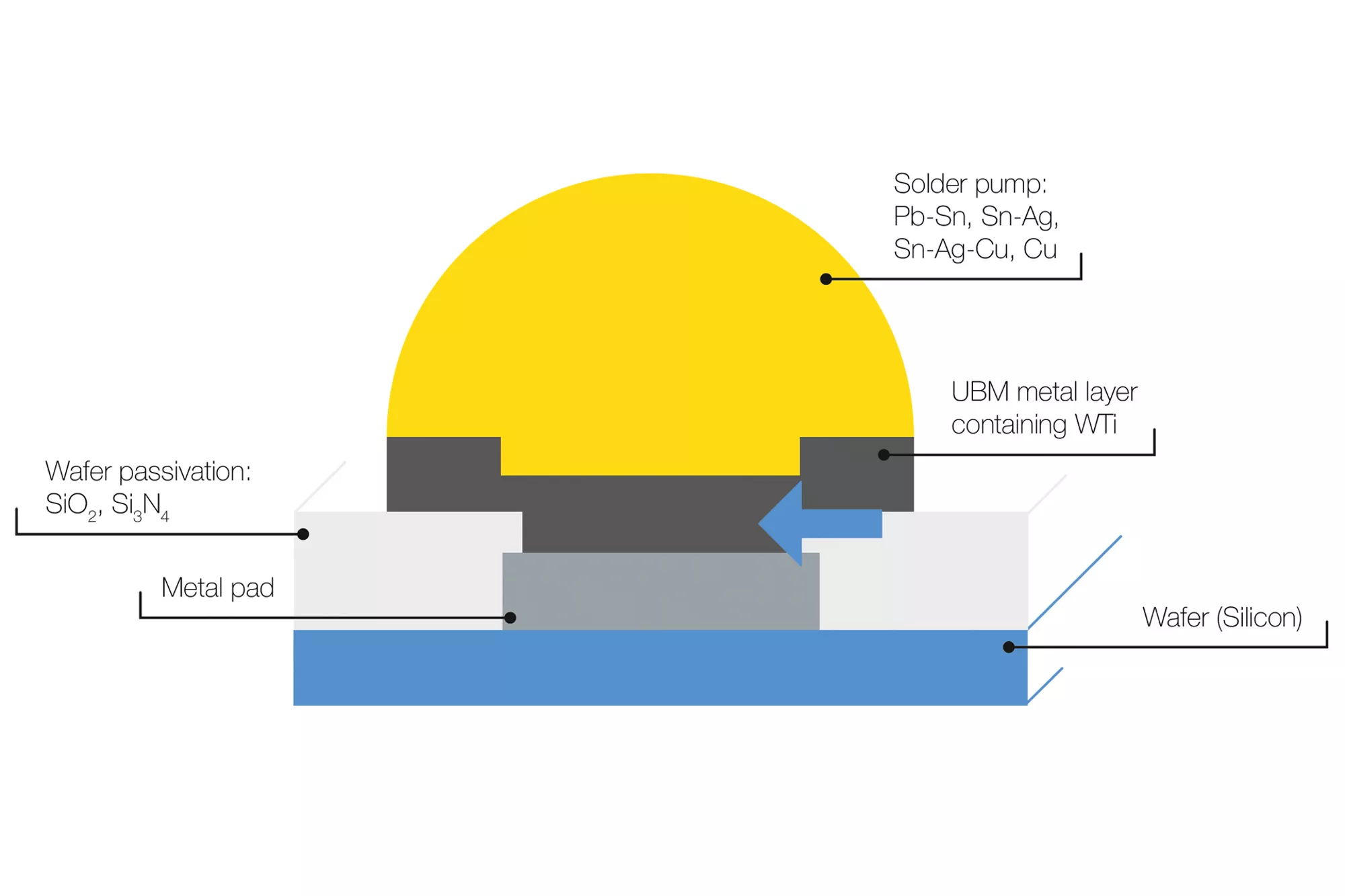
Areas of application for tungsten-titanium
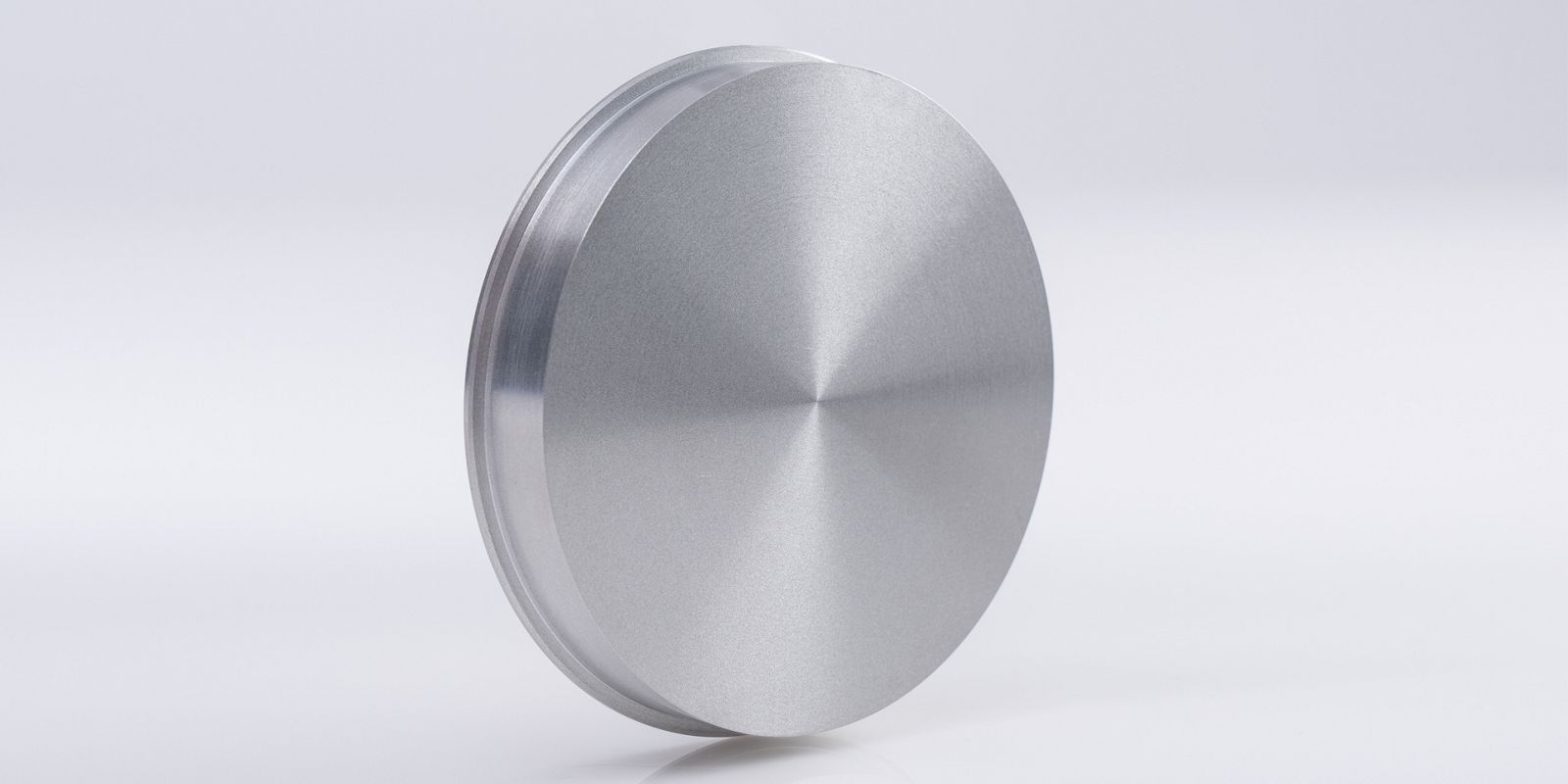
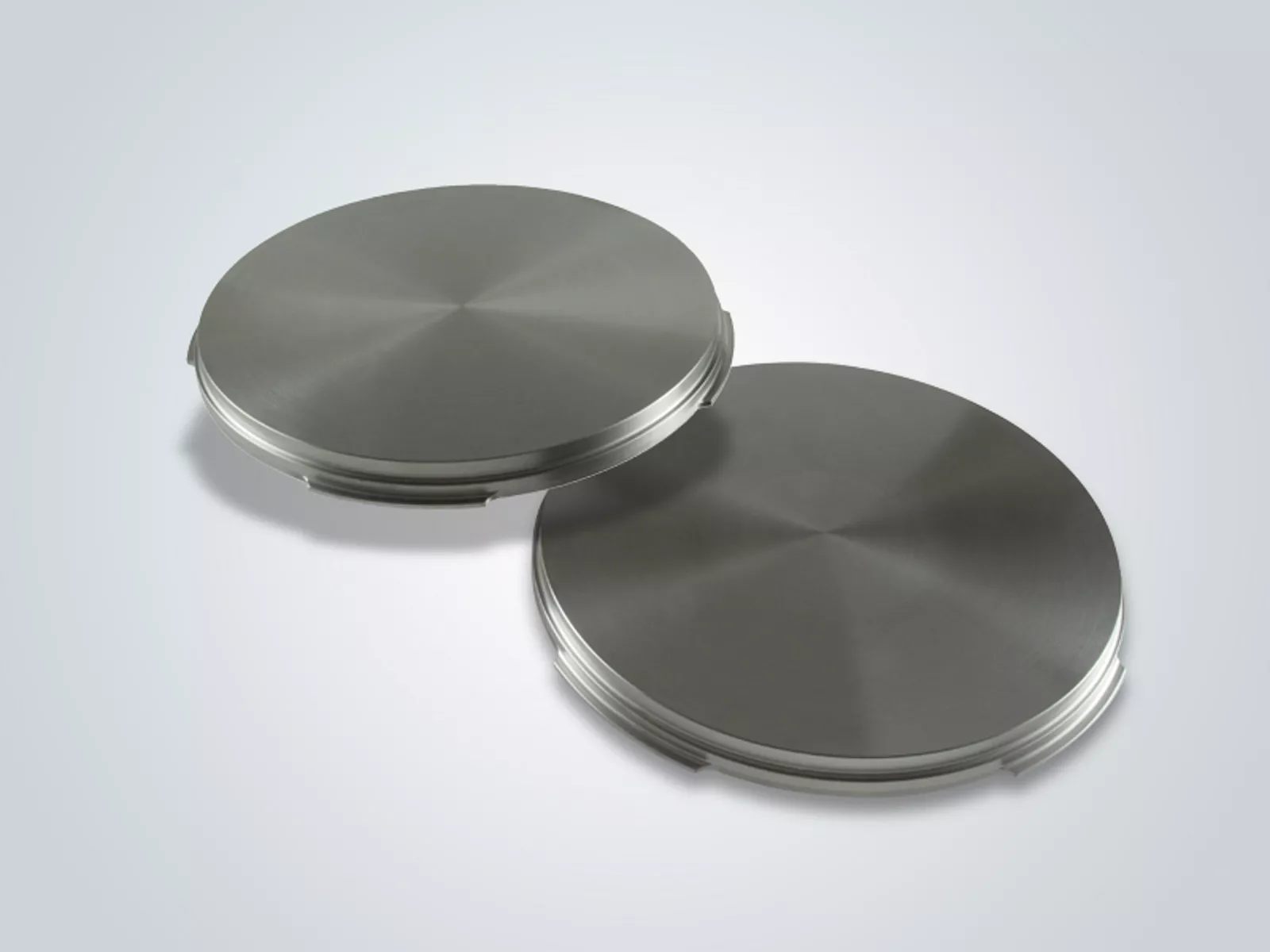
Containing ten percent by weight titanium, tungsten-titanium (WTi) is used as a diffusion barrier and adhesive agent for metallization in microchips. In this area of application, WTi separates the semiconductor and metallization layers, e.g., aluminum from silicon or copper from silicon. Without diffusion barriers, copper and silicon would form an intermetallic phase in microchips and thereby impair the function of the semiconductor. In the case of flexible thin-film solar cells (CIGS), a WTi barrier layer prevents iron atoms from diffusing from the steel substrate through the molybdenum back contact and into the CIGS semiconductor. Just a few µg/g of iron can significantly reduce the efficiency of CIGS solar cells.